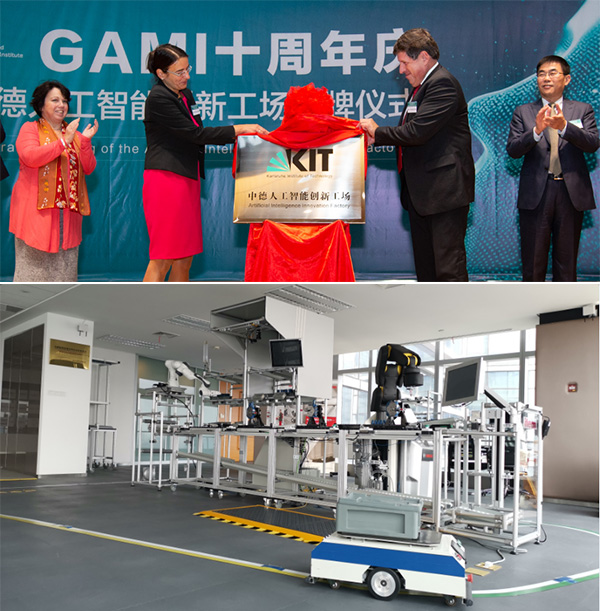
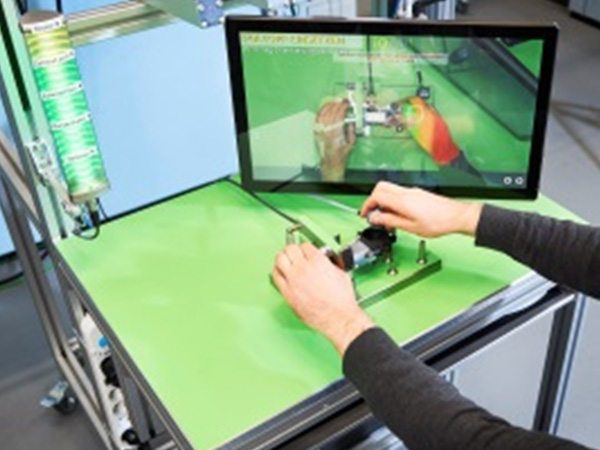
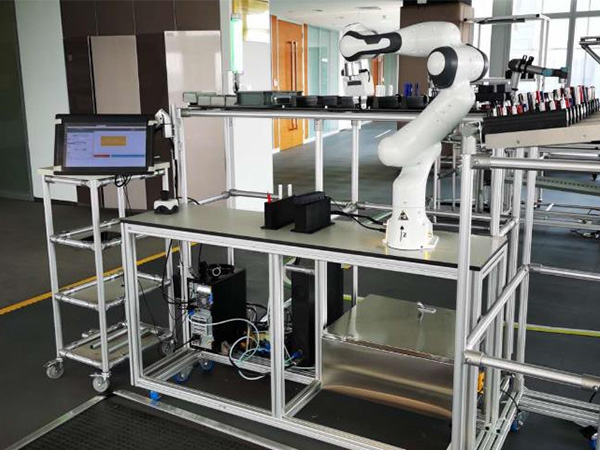
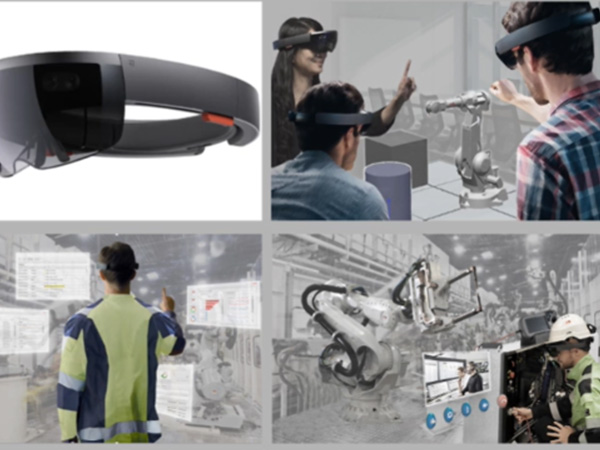
The industry world uses many automation systems to achieve massive production by the repeatability that it allows. However, traditional robotic systems are not suitable for every task that each production requires. There are tasks that involves uncertainties and demand cognitive knowledge, that only humans can provide. Contrarily, humans do not have the same speed, stamina and physical strength as robots do. This duality leads to an idealization of a co-working between humans and robots in a way that both of the contributors could make use of their own values and not be limited by their own conditions. This combination of working is addressed as Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC).